The goal of this page is to learn how Kerberos works in an Active Directory environment.
How it works ?
Kerberos is used when a client wants to use a service that is exposed on a network, without needing to send his password, and with no need for the server to store the passwords from all the clients. Basically, its a centralized authentication server.
To make this work, three main things are needed:
- A client, which can be a computer, a service or even a person ;
- A server offering a service ;
- And a KDC Key Distribution Center, which is the DC Domain Controller in an AD Active Directory environment.
The main idea behind this, is that when a user wants to access a service, no password will be sent on the network, preventing from leaks that may compromise it. The centralized authentication happens in the KDC.
To do so, the process is divided in three step:
- AS Authentication Service : The client must authenticate himself to the KDC ;
- TGT Ticket-Granting Ticket : He must then ask for a ticket that allows the access to a service ;
- AP Access Permitted : The client finally communicates with the service.
The best exemple for this is when you want to go in a nightclub.
- First, you’ll need to show your ID, before being able to enter the club.
- Then, when everything is good, they will give you a ticket for a drink.
- Finally, you can use this ticket to get your drink from the bar.
Here is a quick schema of how it works when a users requests a service:
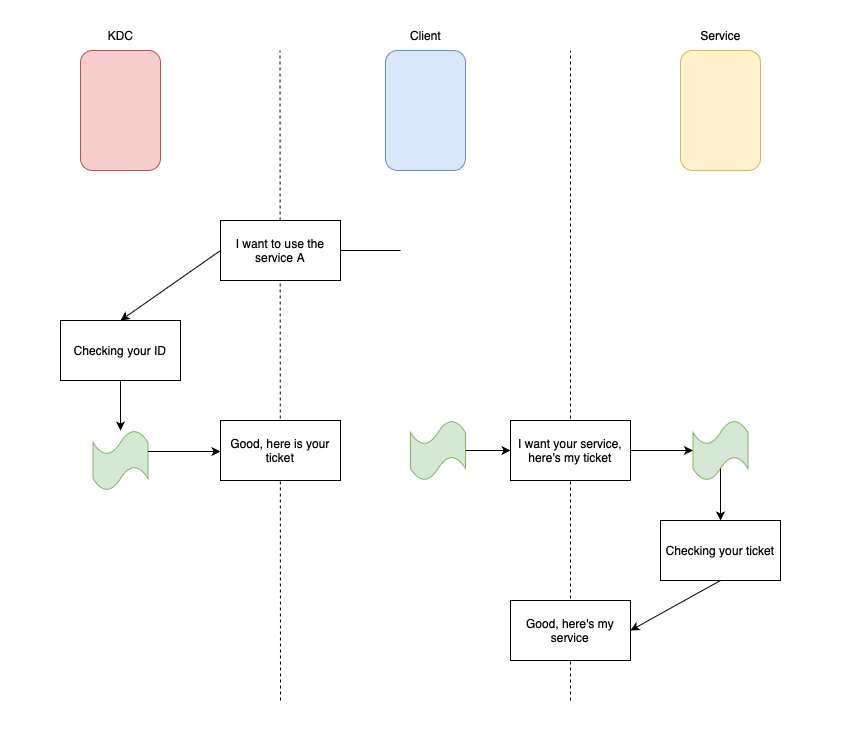
Detailing the steps
So, we’re in an AD context, meaning that the KDC is the DC. The KDC has all the information of the domain, including the secrets of each service, user, machine. Thus, except for the DC, everyone only know his own secret, and therefore do not know the secrets of the other objects in Active Directory.
Here’s our current state:
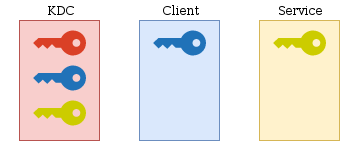
Let’s take a user named john as an example. He wants to use a service on the network. To do so john need to authenticated himself to the KDC,
and then send a request to use the service. This phase is called the AS Authentication Service.
AS : Authentication Service
TODO : Finish this page with the explanation of each step + Wireshark example.